-40%
RPPC Czechoslovakia Czech Republic and Slovakia.WOMENS MARCH POLAND ? PATRIOTIC
$ 7.86
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Czechoslovakia RPPC Czechoslovakia Czech Republic and Slovakia.WOMENS MARCH POLAND ? PATRIOTIC SUFFRAGETTEFrom Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
"Czechoslovak" redirects here. For the communist country, see
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic
. For other uses, see
Czechoslovak (disambiguation)
.
Czechoslovakia
Československo
Česko‑Slovensko
[a]
1918–1939
1945–1992
1939–1945:
Government-in-exile
Flag
(1920–1992)
Lesser coat of arms
(1920–1960)
Motto:
‘
Pravda vítězí
/ Pravda víťazí’
(Czech /
Slovak
, 1918–1990)
’Veritas vincit’
(
Latin
, 1990–1992)
’Truth prevails’
Anthems:
’
Kde domov můj
’
(Czech)
’Where my home is’
MENU
0:00
’
Nad Tatrou sa blýska
’
(Slovak)
’Lightning Over the Tatras’
MENU
0:00
Czechoslovakia during the
interwar period
and the
Cold War
Capital
and largest city
Prague
(
Praha
)
50°05′N
14°25′E
Coordinates
:
50°05′N
14°25′E
Official languages
Czechoslovak
, after 1948
Czech
·
Slovak
Recognised languages
German
Hungarian
Rusyn
Polish
Demonym(s)
Czechoslovak
Government
First Czechoslovak Republic
(1918–1938)
Second Czechoslovak Republic
(1938–1939)
Third Czechoslovak Republic
(1945–1948)
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic
(1948–1990)
Czech and Slovak Federative Republic
(1990–1992)
show
Details
President
• 1918–1935
Tomáš G. Masaryk
•
1935–1938
·
1945–1948
Edvard Beneš
• 1938–1939
Emil Hácha
• 1948–1953
Klement Gottwald
• 1953–1957
Antonín Zápotocký
• 1957–1968
Antonín Novotný
• 1968–1975
Ludvík Svoboda
• 1976–1989
Gustáv Husák
• 1989–1992
Václav Havel
Prime Minister
• 1918–1919
(first)
Karel Kramář
• 1992
(last)
Jan Stráský
Historical era
20th century
•
Proclamation
28 October 1918
•
Munich Agreement
30 September 1938
•
Dissolution
14 March 1939
•
Re-establishment
10 May 1945
•
Coup d'état
25 February 1948
•
Soviet occupation
21 August 1968
•
Velvet Revolution
17 November – 29 December 1989
•
Dissolution
1 January 1993
Area
1921
140,446 km
2
(54,227 sq mi)
1992
127,900 km
2
(49,400 sq mi)
Population
• 1921
13,607,385
• 1992
15,600,000
Currency
Czechoslovak koruna
Calling code
+42
Internet TLD
.cs
Preceded by
Succeeded by
Austria-Hungary
Czech Republic
Slovakia
Today part of
Czech Republic
Slovakia
Ukraine
Calling code +42 was withdrawn in the winter of 1997. The number range was divided between the
Czech Republic
(
+420
) and
Slovak Republic
(
+421
).
Current
ISO 3166-3
code is "CSHH".
Czechoslovakia
, or
Czecho-Slovakia
[1]
(
/
ˌ
tʃ
ɛ
k
oʊ
s
l
oʊ
ˈ
v
æ
k
i
ə
,
-
k
ə
-,
-
s
l
ə
-,
-
ˈ
v
ɑː
-/
;
[2]
[3]
Czech
and
Slovak
:
Československo
,
Česko-Slovensko
),
[4]
[5]
was a
sovereign state
in Central Europe,
[6]
created in October 1918, when it declared its independence from
Austria-Hungary
.
In 1938, after the
Munich Agreement
, the
Sudetenland
became part of
Germany
, while the country lost further territories to
Hungary
and
Poland
. Between 1939 and 1945 the state ceased to exist, as
Slovakia
proclaimed its independence and subsequently the remaining territories in the east became part of
Hungary
, while in the remainder of the
Czech Lands
the German
Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
was proclaimed. In October 1939, after the outbreak of the
Second World War
, former Czechoslovak President,
Edvard Beneš
formed a
government-in-exile
and sought recognition from the
Allies
.
After the end of the war, the pre-1938 Czechoslovakia was reestablished, with the exception of
Carpathian Ruthenia
, which became part of the
Soviet Union
. From 1948 to 1989, Czechoslovakia was part of the
Eastern Bloc
with a
command economy
. Its economic status was formalized in membership of
Comecon
from 1949 and its defense status in the
Warsaw Pact
of May 1955. A period of political liberalization in 1968, known as the
Prague Spring
, was violently ended when the
Soviet Union
, assisted by some other Warsaw Pact countries,
invaded
Czechoslovakia. In 1989, as
Marxist–Leninist
governments and
communism
were
ending
all over
Europe
, Czechoslovaks peacefully deposed their
government
in the
Velvet Revolution
; state price controls were removed after a period of preparation.
In January 1993, Czechoslovakia
split
into the two sovereign states of the
Czech Republic
and
Slovakia
.
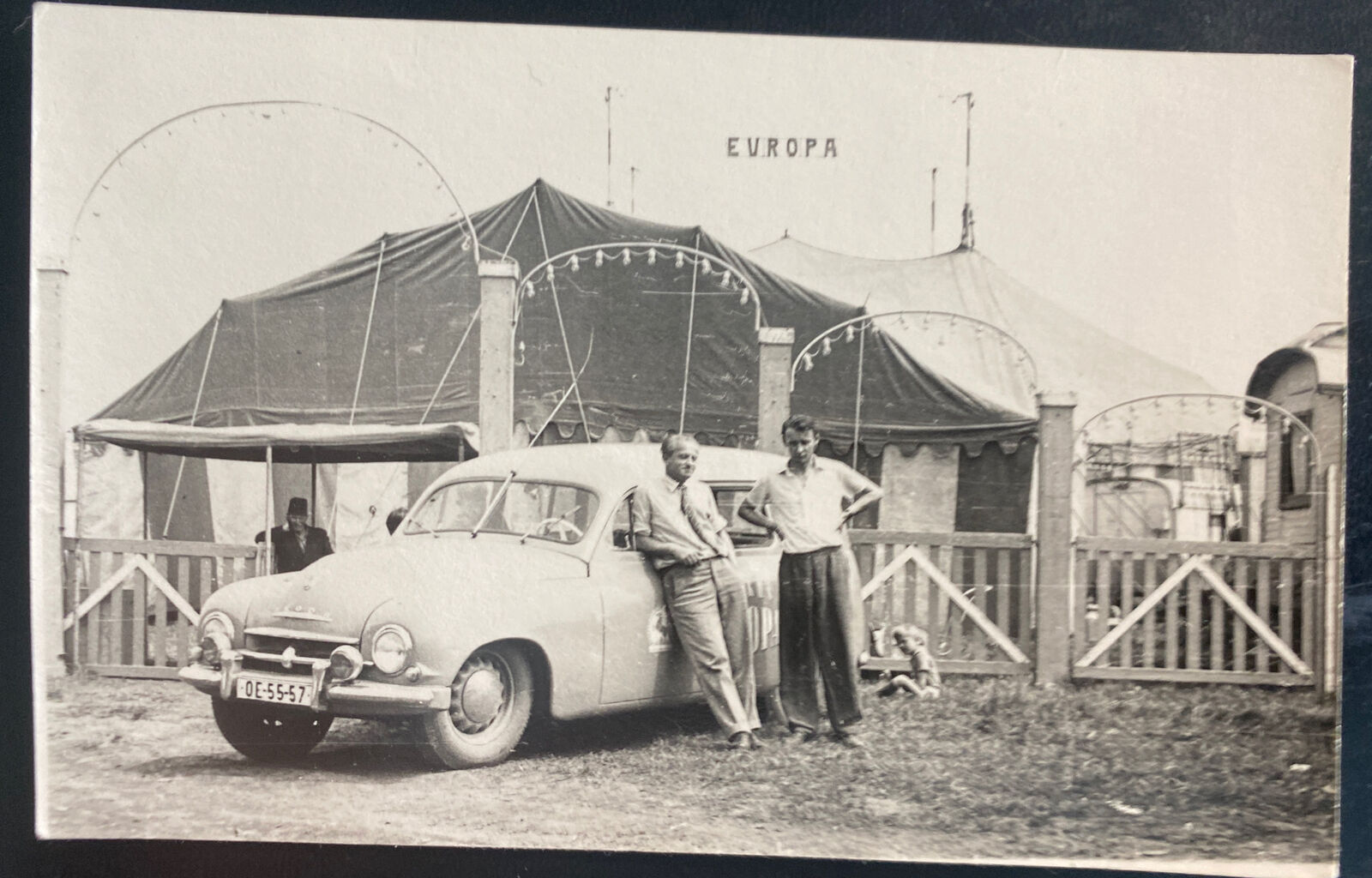
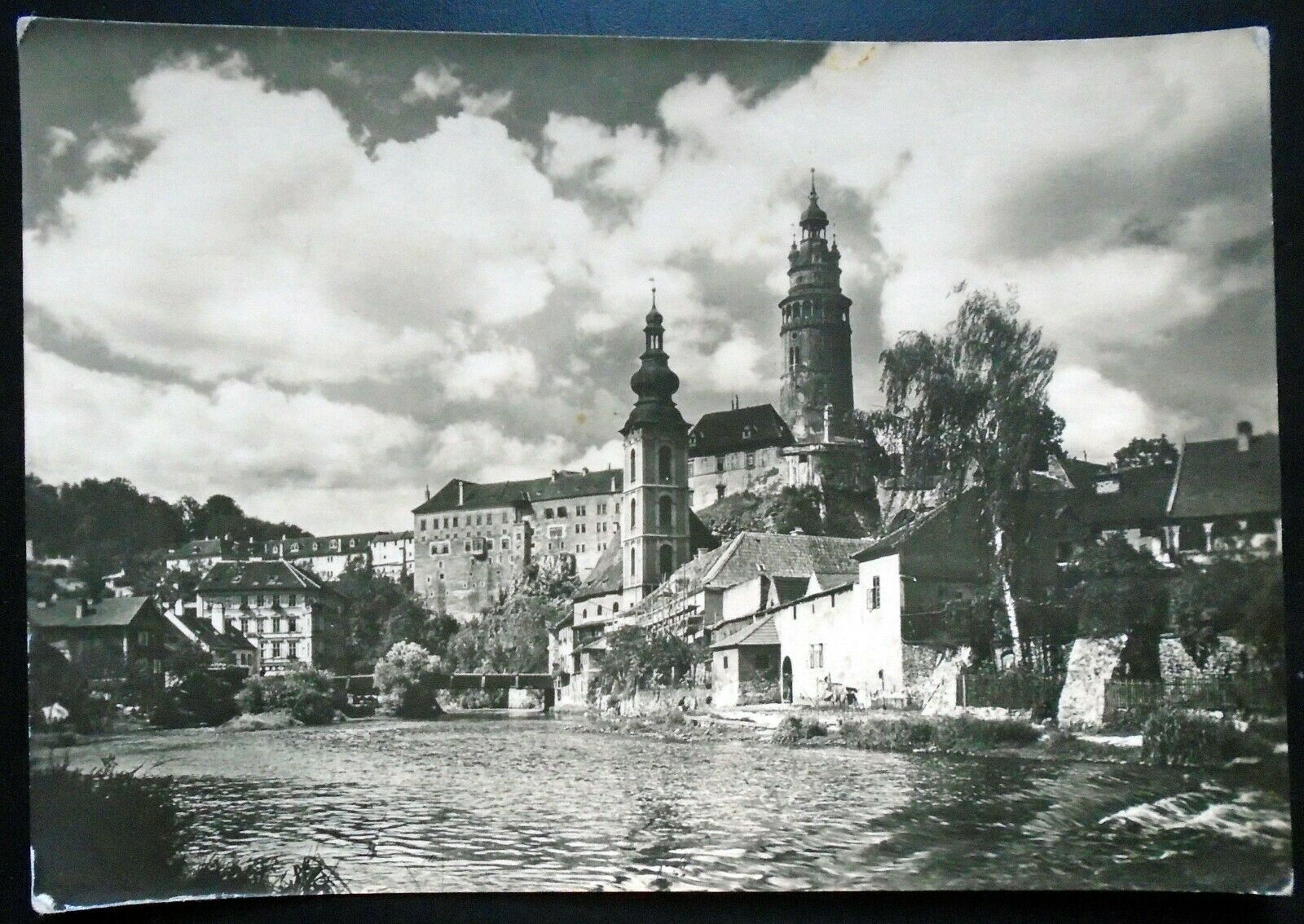
SEE SCAN FOR CONDITION CHECK OUT MY RPPC & REAL PHOTO POSTCARD S
RPPC
NOTE WEAR AND CORNER WEAR LIGHT CREASING
ASK QUESTIONS IF YOU HAVE ANY CONCERNS